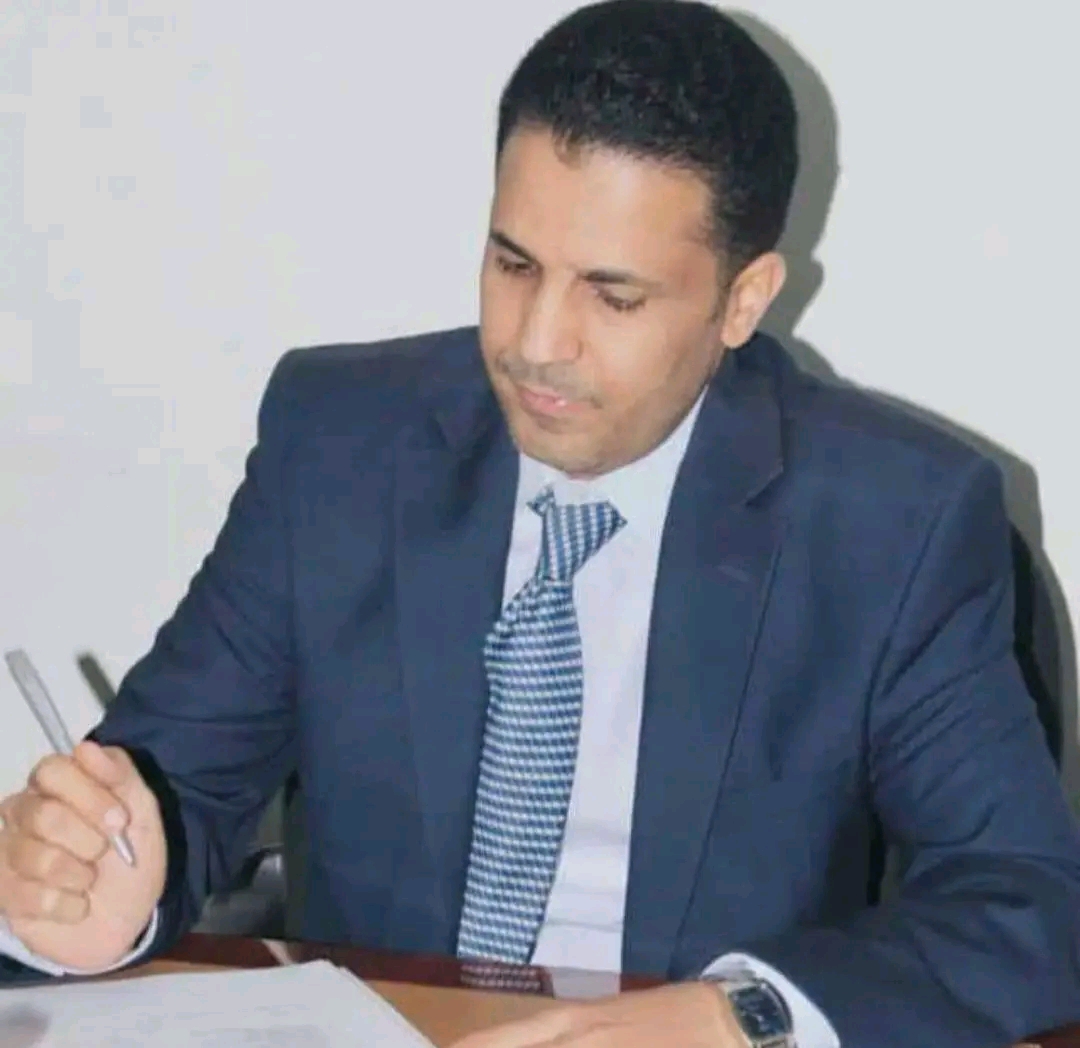
Mogeeb Mosleh Professor of Artificial Intellegence & Data Science
Experienced professional specializing in Artificial Intelligence, Computer Vision, Software Engineering, and Technology Learning. Proficient in Machine Learning, Neural Networks, and Digital Image Processing, with extensive teaching, research, and academic leadership experience across multiple countries.

Client Review